DATE
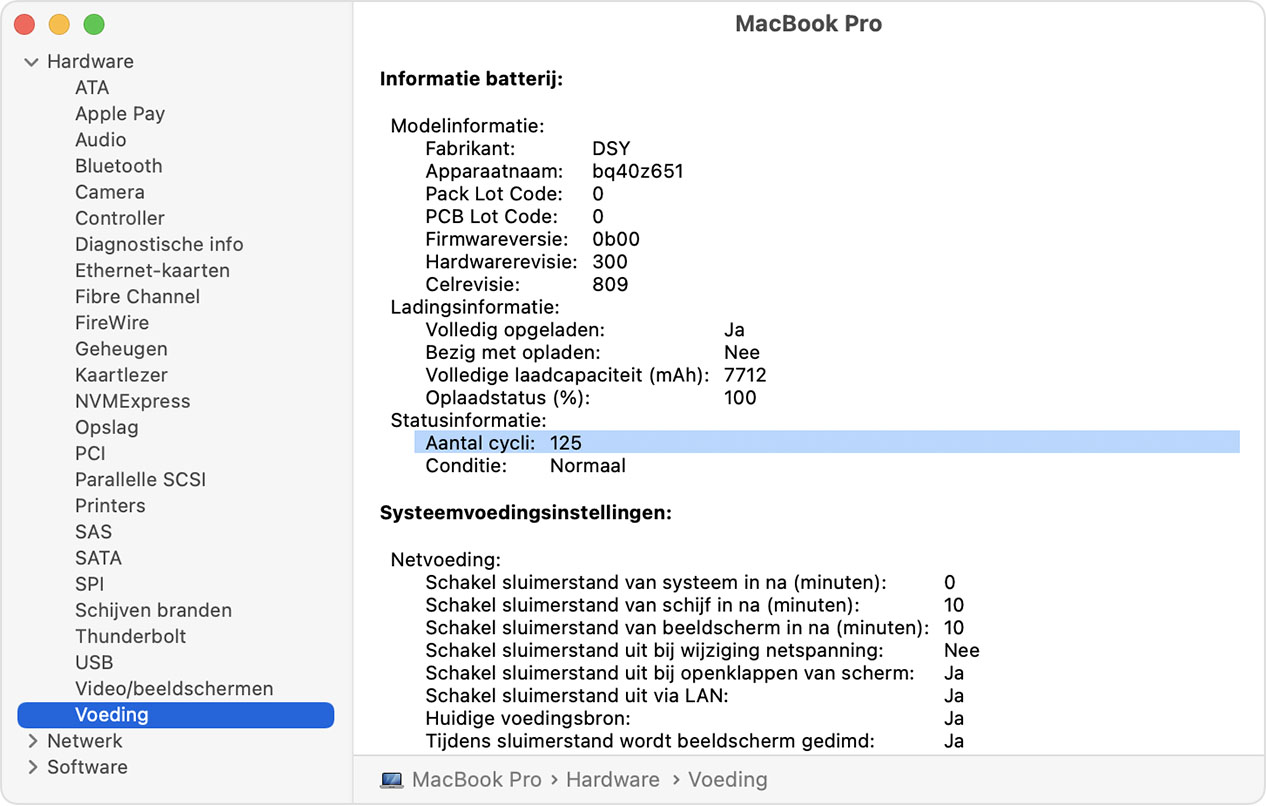
- To Do This In C You Can Use The Sysctl(3) Family Of Functions: Int Count; Size_t Count_len = Sizeof(count); Sysctlbyname('hw.logicalcpu', &count, &...
- System_profiler SPHardwareDataType Shows I Have 1 Processor And 4 Cores. [~] System_profiler SPHardwareDataType Hardware: Hardware Overview:...
Combines separate values for year, month, and day and returns a date/time value.
Jan 02, 2018 The wc command works the same on any modern Unix based operating system, including Mac OS, Linux, FreeBSD, Windows with Bash, and more. Using wc to Count Lines, Words, and Character Counts of a File You can also run the wc command without the -l flag, which will then reveal the line count, the word count, and the character count, in that order. Sep 16, 2011 Weird. I reset it, rebooted, the count didn't increase anymore, but at some point i again found it increasing rapidly. Based on this I assume Mac OS X or something else (like Windows run via bootcamp) sometimes resets that value to 128. My first guess was that maybe it is reset after resuming from sleep, but I couldn't reproduce it by this. Dec 13, 2020 Open your folder in Finder (preferably the one that you want to know the count for). Click on View in the Menu Bar In the top menu bar, click on the View option.
DATEDIF
Returns the number of days, months, or years between two dates.
DATEVALUE
Converts a date text string and returns a date/time value. This function is provided for compatibility with other spreadsheet programs.
DAY
Returns the day of the month for a given date/time value.
DAYNAME
Returns the name of the day of the week from a date/time value or a number. Day 1 is Sunday.
DAYS360
Returns the number of days between two dates based on twelve 30‑day months and a 360‑day year.
EDATE
Returns a date that is some number of months before or after a given date.
EOMONTH
Returns a date that is the last day of the month some number of months before or after a given date.
HOUR
Returns the hour for a given date/time value.
MINUTE
Returns the minutes for a given date/time value.
MONTH
Returns the month for a given date/time value.
MONTHNAME
Returns the name of the month from a number. Month 1 is January.
NETWORKDAYS
Returns the number of working days between two dates. Working days exclude weekends and any other specified dates.
NOW
Returns the current date/time value from the system clock.
SECOND
Returns the seconds for a given date/time value.
TIME
Converts separate values for hours, minutes, and seconds into a date/time value.
TIMEVALUE
Returns the time as a decimal fraction of a 24‑hour day from a given date/time value or from a text string.
TODAY
Returns the current system date. The time is set to 12:00 a.m.
WEEKDAY
Returns a number that is the day of the week for a given date.
WEEKNUM
Returns the number of the week within the year for a given date.
WORKDAY
Returns the date that is the given number of working days before or after a given date. Working days exclude weekends and any other dates specifically excluded.
YEAR
Returns the year for a given date/time value.
YEARFRAC
Finds the fraction of a year represented by the number of whole days between two dates.
DUR2DAYS
Converts a duration value to a number of days.
DUR2HOURS
Converts a duration value to a number of hours.
DUR2MILLISECONDS
Converts a duration value to a number of milliseconds.
DUR2MINUTES
Converts a duration value to a number of minutes.
DUR2SECONDS
Converts a duration value to a number of seconds.
DUR2WEEKS
Converts a duration value to a number of weeks.
DURATION
Combines separate values for weeks, days, hours, minutes, seconds, and milliseconds and returns a duration value.
STRIPDURATION
Evaluates a given value and returns either the number of days represented, if a duration value; or the given value. This function is included for compatibility with other spreadsheet applications.
BASETONUM
Converts a number of the specified base into a number in base 10.
BESSELJ
Returns the integer Bessel function Jn(x).
BESSELY
Returns the integer Bessel function Yn(x).
BIN2DEC
Converts a binary number to the corresponding decimal number.
BIN2HEX
Converts a binary number to the corresponding hexadecimal number.
BIN2OCT
Converts a binary number to the corresponding octal number.
CONVERT
Converts a number from one measurement system to its corresponding value in another measurement system.
DEC2BIN
Converts a decimal number to the corresponding binary number.
DEC2HEX
Converts a decimal number to the corresponding hexadecimal number.
DEC2OCT
Converts a decimal number to the corresponding octal number.
DELTA
Determines whether two values are exactly equal.
ERF
Returns the error function integrated between two values.
ERFC
Returns the complementary ERF function integrated between a given lower bound and infinity.
GESTEP
Determines if one value is greater than or exactly equal to another value.
HEX2BIN
Converts a hexadecimal number to the corresponding binary number.
HEX2DEC
Converts a hexadecimal number to the corresponding decimal number.
HEX2OCT
Converts a hexadecimal number to the corresponding octal number.
NUMTOBASE
Converts a number from base 10 into a number in the specified base.
OCT2BIN
Converts an octal number to the corresponding binary number.
OCT2DEC
Converts an octal number to the corresponding decimal number.
OCT2HEX
Converts an octal number to the corresponding hexadecimal number.
ACCRINT
Calculates the accrued interest added to the purchase price of a security and paid to the seller when the security pays periodic interest.
ACCRINTM
Calculates the total accrued interest added to the purchase price of a security and paid to the seller when the security pays interest only at maturity.
BONDDURATION
Calculates the weighted average of the present value of the cash flows for an assumed par value of $100.
BONDMDURATION
Calculates the modified weighted average of the present value of the cash flows for an assumed par value of $100.
COUPDAYBS
Returns the number of days between the beginning of the coupon period in which settlement occurs and the settlement date.
COUPDAYS
Returns the number of days in the coupon period in which settlement occurs.
COUPDAYSNC
Returns the number of days between the settlement date and the end of the coupon period in which settlement occurs.
COUPNUM
Returns the number of coupons remaining to be paid between the settlement date and the maturity date.
CUMIPMT
Returns the total interest included in loan or annuity payments over a chosen time interval based on fixed periodic payments and a fixed interest rate.
CUMPRINC
Returns the total principal included in loan or annuity payments over a chosen time interval based on fixed periodic payments and a fixed interest rate.
CURRENCY
Returns data from the previous market day's close about the exchange rate between two currencies, retrieved remotely via the Internet.
CURRENCYCODE
Returns the ISO currency code of a given currency value, or the currency code for the language and region set for the computer or for the current document.
CURRENCYCONVERT
Returns the price of a given currency value in a different currency, using exchange rate data from the previous market day's close, retrieved remotely via the Internet.
CURRENCYH
Returns historical data on the exchange rate between two currencies for a given date. The value returned is in the target currency (the currency to which you're converting).
DB
Returns the amount of depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the fixed‑declining balance method.
DDB
Returns the amount of depreciation of an asset based on a specified depreciation rate.
DISC
Returns the annual discount rate of a security that pays no interest and is sold at a discount to its redemption value.
EFFECT
Returns the effective annual interest rate from the nominal annual interest rate based on the number of compounding periods per year.
FV
Returns the future value of an investment based on a series of regular periodic cash flows (payments of a constant amount and all cash flows at constant intervals) and a fixed interest rate.
INTRATE
Returns the effective annual interest rate for a security that pays interest only at maturity.
IPMT
Returns the interest portion of a specified loan or annuity payment based on fixed, periodic payments and a fixed interest rate.
IRR
Returns the internal rate of return for an investment that is based on a series of potentially irregular cash flows that occur at regular time intervals.
ISPMT
Returns the interest portion of a specified loan or annuity payment based on fixed, periodic payments and a fixed interest rate. This function is provided for compatibility with tables imported from other spreadsheet applications.
MIRR
Returns the modified internal rate of return for an investment that is based on a series of potentially irregular cash flows that occur at regular time intervals. The rate earned on positive cash flows and the rate paid to finance negative cash flows can differ.
NOMINAL
Returns the nominal annual interest rate from the effective annual interest rate based on the number of compounding periods per year.
NPER
Returns the number of payment periods for a loan or annuity based on a series of regular periodic cash flows (payments of a constant amount and all cash flows at constant intervals) and a fixed interest rate.
NPV
Returns the net present value of an investment based on a series of potentially irregular cash flows that occur at regular time intervals.
PMT
Returns the fixed periodic payment for a loan or annuity based on a series of regular periodic cash flows (payments of a constant amount and all cash flows at constant intervals) and a fixed interest rate.
PPMT
Returns the principal portion of a specified loan or annuity payment based on fixed periodic payments and a fixed interest rate.
PRICE
Returns the price of a security that pays periodic interest per $100 of redemption (par) value.
PRICEDISC
Returns the price of a security that is sold at a discount to redemption value and does not pay interest per $100 of redemption (par) value.
PRICEMAT
Returns the price of a security that pays interest only at maturity per $100 of redemption (par) value.
PV
Returns the present value of an investment or annuity based on a series of regular periodic cash flows (payments of a constant amount and all cash flows at constant intervals) and a fixed interest rate.
RATE
Returns the interest rate of an investment, loan, or annuity based on a series of regular periodic cash flows (payments of a constant amount and all cash flows at constant intervals) and a fixed interest rate.
RECEIVED
Returns the maturity value for a security that pays interest only at maturity.
SLN
Returns the amount of depreciation of an asset for a single period using the straight‑line method.
STOCK
Returns data from the previous market day's close about a given stock, retrieved remotely via the Internet.
STOCKH
Returns historical price information about a stock for a given date, retrieved remotely via the Internet.
SYD
Returns the amount of depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the sum‑of‑the‑years‑digits method.
VDB
Returns the amount of depreciation of an asset over a chosen time interval, based on a specified depreciation rate.
XIRR
Returns the internal rate of return for an investment that is based on a series of irregularly spaced cash flows.
XNPV
Returns the present value of an investment or annuity based on a series of irregularly spaced cash flows and at a discount interest rate.
YIELD
Returns the effective annual interest rate for a security that pays regular periodic interest.
YIELDDISC
Returns the effective annual interest rate for a security that is sold at a discount to redemption value and pays no interest.
YIELDMAT
Returns the effective annual interest rate for a security that pays interest only at maturity.
AND
Returns TRUE if all arguments are true; otherwise it returns FALSE.
FALSE
Returns the Boolean value FALSE. This function is included for compatibility with tables imported from other spreadsheet applications.
IF
Returns one of two values depending on whether a specified expression evaluates to a Boolean value of TRUE or FALSE.
IFERROR
Returns a value that you specify if a given value evaluates to an error; otherwise it returns the given value.
IFS
Checks specified expressions returns a value based on the first condition that evaluates to a boolean value of TRUE.
ISBLANK
Returns TRUE if the specified cell is empty; otherwise it returns FALSE.
ISDATE
Returns the boolean value TRUE if the given expression evaluates to a date and the boolean value FALSE otherwise.
ISERROR
Returns TRUE if a given expression evaluates to an error; otherwise it returns FALSE.
ISEVEN
Returns TRUE if the value is even (leaves no remainder when divided by 2); otherwise it returns FALSE.
ISNUMBER
Returns the boolean value TRUE if the given expression evaluates to a number and the boolean value FALSE otherwise.
ISODD
Returns TRUE if the value is odd (leaves a remainder when divided by 2); otherwise it returns FALSE.
ISTEXT
Returns the boolean value TRUE if the given expression evaluates to a string and the boolean value FALSE otherwise.
NOT
Returns the opposite of the Boolean value of a specified expression.
OR
Returns TRUE if any argument is true; otherwise it returns FALSE.
TRUE
Returns the Boolean value TRUE. This function is included for compatibility with tables imported from other spreadsheet applications.
ABS
Returns the absolute value of a number or duration.
CEILING
Rounds a number away from zero to the nearest multiple of the specified factor.
COMBIN
Returns the number of different ways you can combine a number of items into groups of a specific size, ignoring the order within the groups.
EVEN
Rounds a number away from zero to the next even number.
EXP
Returns e (the base of natural logarithms) raised to the specified power.
FACT
Returns the factorial of a number.
FACTDOUBLE
Returns the double factorial of a number.
FLOOR
Rounds a number toward zero to the nearest multiple of the specified factor.
GCD
Returns the greatest common divisor of the specified numbers.
INT
Returns the nearest integer that is less than or equal to the number.
LCM
Returns the least common multiple of the specified numbers.
LN
Returns the natural logarithm of a number, the power to which e must be raised to result in the number.
LOG
Returns the logarithm of a number using a specified base.
LOG10
Returns the base‑10 logarithm of a number.
MOD
Returns the remainder from a division.
MROUND
Rounds a number to the nearest multiple of a specified factor.
MULTINOMIAL
Returns the closed form of the multinomial coefficient of the given numbers.
ODD
Rounds a number away from zero to the next odd number.
PI
Returns the approximate value of π (pi), the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter.
POLYNOMIAL
Evaluates a polynomial at a given point.
POWER
Returns a number raised to a power.
PRODUCT
Returns the product of one or more numbers.
QUOTIENT
Returns the integer quotient of two numbers.
RAND
Returns a random number that is greater than or equal to 0 and less than 1.
RANDBETWEEN
Returns a random integer within the specified range.
ROMAN
Converts a number to Roman numerals.
ROUND
Returns a number rounded to the specified number of places.
ROUNDDOWN
Returns a number rounded toward zero (rounded down) to the specified number of places.
ROUNDUP
Returns a number rounded away from zero (rounded up) to the specified number of places.
SERIESSUM
Computes and returns the sum of a power series.
SIGN
Returns 1 when a given number is positive, –1 when it is negative, and 0 when it is zero.
SQRT
Returns the square root of a number.
SQRTPI
Returns the square root of a number multiplied by π (pi).
SUM
Returns the sum of a collection of numbers.
SUMIF
Returns the sum of a collection of numbers, including only numbers that satisfy a specified condition.
SUMIFS
Returns the sum of the cells in a collection where the test values meet the given conditions.
SUMPRODUCT
Returns the sum of the products of corresponding numbers in one or more ranges.
SUMSQ
Returns the sum of the squares of a collection of numbers.
SUMX2MY2
Returns the sum of the difference of the squares of corresponding values in two collections.
SUMX2PY2
Returns the sum of the squares of corresponding values in two collections.
SUMXMY2
Returns the sum of the squares of the differences between corresponding values in two collections.
TRUNC
Truncates a number to the specified number of digits.
ADDRESS
Constructs a cell address string from separate row, column, and table identifiers.
AREAS
Returns the number of ranges the function references.
CHOOSE
Returns a value from a collection of values based on a specified index value.
COLUMN
Returns the column number of the column containing a specified cell.
COLUMNS
Returns the number of columns included in a specified range of cells.
HLOOKUP
Returns a value from a range of rows by using the top row of values to pick a column and a row number to pick a row within that column.
INDEX
Returns the value in the cell located at the intersection of the specified row and column within a range of cells.
INDIRECT
Returns the contents of a cell or range referenced by an address specified as a string.
INTERSECT.RANGES
Returns a range that is the intersection of the specified ranges.
LOOKUP
Finds a match for a given search value in one range, then returns the value in the cell with the same relative position in a second range.
MATCH
Returns the position of a value within a range.
OFFSET
Returns a range of cells that is the specified number of rows and columns away from the specified base cell.
ROW
Returns the row number of the row containing a specified cell.
ROWS
Returns the number of rows included in a specified range of cells.
TRANSPOSE
Returns a vertical range of cells as a horizontal range of cells, or vice versa.
UNION.RANGES
Returns a range that represents a range representing the union of the specified ranges.
VLOOKUP
Returns a value from a range of columns by using the left column of values to pick a row and a column number to pick a column in that row.
XLOOKUP
Searches a range for a specified value and returns the value from the same row in another column.
AVEDEV
Returns the average of the difference of a collection of numbers from their average (arithmetic mean).
AVERAGE
Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of a collection of numbers.
AVERAGEA
Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of a collection of values, including text and Boolean values.
AVERAGEIF
Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of the cells in a range that meet a given condition.
AVERAGEIFS
Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of the cells in a collection that meet all the given conditions.
BETADIST
Returns the cumulative beta distribution probability value.
BETAINV
Returns the inverse of the given cumulative beta distribution probability value.
BINOMDIST
Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability of the specified form.
CHIDIST
Returns the one‑tailed probability of the chi‑square distribution.
CHIINV
Returns the inverse of the one‑tailed probability of the chi‑square distribution.
CHITEST
Returns the value from the chi‑square distribution for the given data.
CONFIDENCE
Returns a value for creating a statistical confidence interval for a sample from a population with a known standard deviation.
CORREL
Returns the correlation between two collections using linear regression analysis.
COUNT
Returns the number of its arguments that contain numbers, numeric expressions, or dates.
COUNTA
Returns the number of its arguments that are not empty.
COUNTBLANK
Returns the number of cells in a range that are empty.
COUNTIF
Returns the number of cells in a range that satisfy a given condition.
COUNTIFS
To Do This In C You Can Use The Sysctl(3) Family Of Functions: Int Count; Size_t Count_len = Sizeof(count); Sysctlbyname('hw.logicalcpu', &count, &...
Returns the number of cells in one or more ranges that satisfy given conditions (one condition per range).
COVAR
Returns the covariance of two collections.
CRITBINOM
Returns the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is greater than or equal to a given value.
DEVSQ
Returns the sum of the squares of deviations of a collection of numbers from their average (arithmetic mean).
EXPONDIST
Returns the exponential distribution of the specified form.
FDIST
Returns the F probability distribution.
FINV
Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution.
FORECAST
Returns the forecasted y value for a given x value based on sample values using linear regression analysis.
FREQUENCY
Returns an array of how often data values occur within a range of interval values.
GAMMADIST
Returns the gamma distribution in the specified form.
GAMMAINV
Returns the inverse gamma cumulative distribution.
GAMMALN
Returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, G(x).
GEOMEAN
Returns the geometric mean.
HARMEAN
Returns the harmonic mean.
INTERCEPT
Returns the y‑intercept of the best‑fit line for the collection using linear regression analysis.
LARGE
Returns the nth‑largest value within a collection. The largest value is ranked number 1.
LINEST
Returns an array of the statistics for a straight line that best fits the given data using the least squares method.
LOGINV
Returns the inverse of the log‑normal cumulative distribution function of x.
LOGNORMDIST
Returns the log‑normal distribution.
MAX
Returns the largest number in a collection.
MAXA
Returns the largest number in a collection of values that may include text and Boolean values.
MEDIAN
Returns the median value in a collection of numbers. The median is the value where half the numbers in the collection are less than the median and half are greater.
MIN
Returns the smallest number in a collection.
MINA
Returns the smallest number in a collection of values that may include text and Boolean values.
MODE
Returns the most frequently occurring value in a collection of numbers.
NEGBINOMDIST
Returns the negative binomial distribution.
NORMDIST
Returns the normal distribution of the specified function form.
NORMINV
Returns the inverse of the cumulative normal distribution.
NORMSDIST
Returns the standard normal distribution.
NORMSINV
Returns the inverse of the cumulative standard normal distribution.
PERCENTILE
Returns the value within a collection that corresponds to a particular percentile.
PERCENTRANK
Returns the rank of a value in a collection as a percentage of the collection.
PERMUT
Returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects that can be selected from a total number of objects.
POISSON
Returns the probability that a specific number of events will occur using the Poisson distribution.
PROB
Returns the probability of a range of values if you know the probabilities of the individual values.
QUARTILE
Returns the value for the specified quartile of a given collection.
RANK
Returns the rank of a number within a range of numbers.
SLOPE
Returns the slope of the best‑fit line for the collection using linear regression analysis.
SMALL
Returns the nth‑smallest value within a range. The smallest value is ranked number 1.
STANDARDIZE
Returns a normalized value from a distribution characterized by a given mean and standard deviation.
STDEV
Returns the standard deviation, a measure of dispersion, of a collection of values based on their sample (unbiased) variance.
STDEVA
Returns the standard deviation, a measure of dispersion, of a collection of values that may include text and Boolean values, based on the sample (unbiased) variance.
STDEVP
Returns the standard deviation, a measure of dispersion, of a collection of values based on their population (true) variance.
STDEVPA
Returns the standard deviation, a measure of dispersion, of a collection of values that may include text and Boolean values, based on the population (true) variance.
TDIST
Returns the probability from the Student's t‑distribution.
TINV
Returns the t value (a function of the probability and degrees of freedom) from the Student's t‑distribution.
TTEST
Returns the probability associated with a Student's t‑test, based on the t‑distribution function.
VAR
Returns the sample (unbiased) variance, a measure of dispersion, of a collection of values.
VARA
Returns the sample (unbiased) variance, a measure of dispersion, of a collection of values, including text and Boolean values.
VARP
Returns the population (true) variance, a measure of dispersion, of a collection of values.
VARPA
Returns the sample (unbiased) variance, a measure of dispersion, of a collection of values, including text and Boolean values.
WEIBULL
Returns the values of the Weibull distribution.
ZTEST
Returns the one‑tailed probability value of the Z‑test.
CHAR
Returns the character that corresponds to a decimal Unicode character code.
CLEAN
Removes most common nonprinting characters (Unicode character codes 0–31) from text.
CODE
Returns the decimal Unicode number of the first character in a specified string.
CONCATENATE
Joins (concatenates) strings.
COUNTMATCHES
Returns a number value representing the number of times a given substring appears in the original string value.
DOLLAR
Returns a string formatted as a dollar amount from a given number.
EXACT
Returns TRUE if the argument strings are identical in case and content.
FIND
Returns the starting position of one string within another.
FIXED
Rounds a number to the specified number of decimal places and then returns the result as a string value.
LEFT
Returns a string consisting of the specified number of characters from the left end of a given string.
LEN
Returns the number of characters in a string.
LOWER
Returns a string that is entirely lowercase, regardless of the case of the characters in the specified string.
MID
Returns a string consisting of the given number of characters from a string starting at the specified position.
PLAINTEXT
Returns a string value stripped of any rich text attributes in the input value.
PROPER
Returns a string where the first letter of each word is uppercase and all remaining characters are lowercase, regardless of the case of the characters in the specified string.
REGEX
Enables usage of regular expressions in other text and conditional functions. It can be used with all functions that expect a condition (IF, COUNTIF, …) or a string match (SUBSTITUTE, TEXTBEFORE, …). When not used as a condition or to match text, REGEX returns the underlying regular expression as a string value.
REGEX.EXTRACT
Returns the matches or capture groups in a match of a given regular expression in a source string.
REPLACE
Returns a string where a specified number of characters of a given string have been replaced with a new string.
REPT
Returns a string that contains a given string repeated a specified number of times.
RIGHT
Returns a string consisting of the given number of characters from the right end of a specified string.
SEARCH
Returns the starting position of one string within another, ignoring case and allowing wildcards.
SUBSTITUTE
Returns a string where the specified characters of a given string have been replaced with a new string.
TEXTAFTER
Returns a string value consisting of all characters that appear after a given substring in the original string value.
TEXTBEFORE
Returns a string value consisting of all characters that appear before a given substring in the original string value.
TEXTBETWEEN
Returns a string value consisting of all characters that appear between two given substrings in the original string value.
T
Returns the text contained in a cell. This function is included for compatibility with tables imported from other spreadsheet applications.
TRIM
Returns a string based on a given string, after removing extra spaces.
UPPER
Returns a string that is entirely uppercase, regardless of the case of the characters in the specified string.
VALUE
Returns a number value even if the argument is formatted as text.
ACOS
Returns the inverse cosine (arccosine) of a number.
ACOSH
Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine (hyperbolic arccosine) of a number.
ASIN
Returns the arcsine (the inverse sine) of a number.
ASINH
Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number.
ATAN
Returns the inverse tangent (arctangent) of a number.
ATAN2
Returns the angle, relative to the positive x‑axis, of the line passing through the origin and the specified point.
ATANH
Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number.
COS
Returns the cosine of an angle that is expressed in radians.
COSH
Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a number.
DEGREES
Returns the number of degrees in an angle expressed in radians.
RADIANS
System_profiler SPHardwareDataType Shows I Have 1 Processor And 4 Cores. [~] System_profiler SPHardwareDataType Hardware: Hardware Overview:...
Returns the number of radians in an angle expressed in degrees.
SIN
Returns the sine of an angle that is expressed in radians.
SINH
Returns the hyperbolic sine of the specified number.
TAN
Returns the tangent of an angle that is expressed in radians.
TANH
Returns the hyperbolic tangent of the specified number.
Contents:
Files and Directories
Table A-1 describes the files anddirectories you may find in your root directory.The remaining tables in this chapter describe significantsubdirectories.
Table A-1. Mac OS X's root directory
File or directory | Description |
|---|---|
.DS_Store | This file contains Finder settings, such as icon location and windowsize. The file will appear in any directory thatyou've viewed with the Finder. |
.Trashes/ | This directory contains files that have been dragged to the Trash. Ona boot volume, such files are stored in~/.Trash. On a non-boot volume, these files are in/.Trashes/uid/. |
.hidden | This file contains a list of files that should be invisible to theFinder. |
.vol/ | This directory maps HFS+ file IDs to files. If you know afile's ID, you can open it using/.vol/id. |
Applications (Mac OS 9)/ | This directory contains all your OS 9 applications, ifyou've got Mac OS X and Mac OS 9 installed. |
Applications/ | This directory holds all your Mac OS X applications. ItsUtilities subdirectory includes lots of usefulthings, such as Terminal and Console. |
Desktop DB | This file, along with Desktop DF, contains thedesktop database that is rebuilt when you click Rebuild Desktop inSystem Preferences Classic. |
Desktop DF | See Desktop DB. |
Desktop Folder/ | This directory is the Mac OS 9 desktop folder. |
Developer/ | This directory contains Apple's Developer Tools anddocumentation. This is only available if you have installed theDeveloper Tools. |
Documents/ | This is the Mac OS 9 documents folder. |
Library/ | This directory contains support files for locally installedapplications, among other things. See Table A-4, later in thischapter. |
Network/ | This directory contains network-mountedApplication, Library, andUsers directories, as well as aServers directory, which contains directoriesmounted by the automount daemon. |
Shared Items/ | In Mac OS 9, this folder gave multiuser systems a place where userscould store files that other users could access. |
System Folder/ | This is the Mac OS 9 System Folder. |
System/ | This directory contains a subdirectory, Library,which holds support files for the system and system applications,among other things. See Table A-3, later in this chapter. |
Temporary Items/ | This directory contains temporary files used by Mac OS 9. |
TheVolumeSettingsFolder/ | This directory keeps track of details such as open windows anddesktop printers. |
Trash/ | This directory is where Mac OS 9 stores deleted files until the Trashis emptied. |
Users/ | This directory contains home directories for the users on the system.The root user's home directoryis /var/root. |
VM Storage | This is the Mac OS 9 virtual memory file. |
Volumes/ | This directory contains all mounted filesystems, including removablemedia and mounted disk images. |
automount/ | This directory handles static NFS mounts for theautomount daemon. |
bin/ | This directory contains essential system binaries. |
cores/ | This directory is a symbolic link (or symlink)to /private/cores. If core dumps are enabled(with tcsh'slimit andbash/sh'sulimit commands--see thetcsh and bash manpages formore details), they will be created in this directory ascore.pid. |
dev/ | This directory contains files that represent various devices. SeeTable A-6, later in this chapter. |
etc/ | This directory contains system configuration files. See Table A-2,later in this chapter. The directory is a symbolic link to/private/etc. |
lost+found | This directory stores orphaned files discovered byfsck. |
mach | This is a symbolic link to the /mach.sym file. |
mach.sym | This file contains kernel symbols. It is generated during each bootby /etc/rc. |
mach_kernel | This is the Darwin kernel. See Chapter 7 for more information about the kernel. |
private/ | This private directory contains the tmp,var, etc, andcores directories. |
sbin/ | This directory contains executables for system administration andconfiguration. |
tmp/ | This directory holds temporary files. It is a symbolic link to/private/tmp. |
usr/ | This directory contains BSD Unix applications and support files. |
var/ | This directory contains frequently modified files, such as log files.It is a symbolic link to /private/var. |
A.1.1. The /etc Directory
The /etcdirectory contains configuration files for Unix applications andservices, as well as scripts that control system startup. Table A-2lists the contents of the /etc directory.
Table A-2. The /etc directory
File or directory | Description |
|---|---|
6to4.conf | Configuration file for encapsulating IPv6 within IPv4. Seeip6config(8). |
X11/ | X11 configuration directory. This will be present only if you haveinstalled XDarwin. |
acgid/ | File that contains configuration files foracgid, a bridge between Apache and ACGI-capablescripting languages, such as AppleScript. Mac OS X Server only. Forequivalent functionality under Mac OS X, seehttp://www.sentman.com/acgi/. |
afpovertcp.cfg | File that causes Mac OS X to use TCP/IP as the default transport forApple File Protocol (AFP). Use this file to configure the defaultsfor AFP over TCP/IP. |
appletalk.cfg | AppleTalk configuration file for routing or multihoming. See theappletalk.cfg(5) manpage. |
authorization | File that controls how applications, such as installers, cantemporarily obtain root privileges. |
bashrc | Global configuration file for bash, theBourne-again shell. |
crontab | root'scrontab. See Section 2.3.1. |
csh.cshrc | Global csh configuration file, processed whenthe shell starts up. If you have a .cshrc or.tcshrc file in your home directory,tcsh will execute its contents as well. |
csh.login | Global csh login file, processed when a loginshell starts up. If you have a .login file inyour home directory, tcsh will execute itscontents as well. |
csh.logout | Global csh logout file, processed when a userlogs out of a login shell. |
cups/ | Directory that contains configuration files for Common Unix PrintingSystem (CUPS). |
daily | cron job that is run once a day (seecrontab). This is a symlink to/etc/periodic/daily/500.daily. |
defaults/ | Directory that contains default configuration files for applicationsand utilities. |
diskspacemonitor/ | Configuration files for diskspacemonitor, whichmonitors the amount of free disk space. Mac OS X Server only. |
dumpdates | Dump date records created by dump(5), which isrun by /etc/daily. |
find.codes | Description not available at time of writing; see errata page athttp://www.oreilly.com/catalog/mosxgeeks. |
ftpusers | List of users who are prohibited from using FTP. |
gdb.conf | Global gdb configuration file. |
gettytab | Terminal configuration database. |
group | Group permissions file. See Chapter 3 for moreinformation. |
hostconfig | System configuration file that controls many of the startup itemsdescribed in Section 2.1.4 in Chapter 2. |
hosts | Host database; a mapping of IP addresses to hostnames. You can usethis as a supplement to other Directory Services, such as DNS. Mac OSX 10.1 and earlier consulted this file only in single-user mode, butMac OS X 10.2 (Jaguar) uses this file at other times. For moreinformation, see Chapter 3. |
hosts.equiv | List of trusted remote hosts and host-user pairs. This is used byrsh and is inherently insecure. You should usessh instead, which is a secure alternative. Seessh-keygen(1) to generate key pairs that can beused to set up a trust relationship with remote users. |
hosts.lpd | List of hosts that are allowed to connect to the Unixlpd service. |
httpd/ | Directory that contains Apache's configuration files. |
iftab | Configuration file for network interfaces. |
inetd.conf | Internet super-server (inetd) configurationfile. |
IPAliases | Configuration file for IP aliases. |
kcpassword | Description not available at time of writing; see errata page athttp://www.oreilly.com/catalog/mosxgeeks. |
kern_loader.conf | Description not available at time of writing; see errata page athttp://www.oreilly.com/catalog/mosxgeeks. |
localtime | Symbolic link to your system's time zone, such as:/usr/share/zoneinfo/US/Eastern. |
magic | Database of magic numbers used by the filecommand to determine a file's type. |
mail/ | Directory that contains configuration files forsendmail. Note that Open Directory handles themail aliases (see Chapter 3). |
mail.rc | Global configuration file for /usr/bin/mail. |
manpath.config | Configuration file for man. |
master.passwd | Shadow passwd file. This is consulted only insingle-user mode. During normal system operation, Open Directorymanages user information (see Chapter 3). |
moduli | System-wide prime numbers used for cryptographic applications such asssh. |
monthly | Monthly cron job (seecrontab). This is a symlink to/etc/periodic/monthly/500.monthly. |
motd | Message of the day. This is displayed each time you launch a newTerminal or log in remotely. |
named.conf | Configuration file for named, the DNS daemon.For more details, see named(8). |
networks | Network name database. |
ntp.conf | Configuration file for the Network Time Protocol daemon, whichsynchronizes system time by accessing a remote server. |
openldap/ | Directory that contains configuration files for OpenLDAP, animplementation of the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol. |
pam.d/ | Directory that contains configuration files for PAM . |
passwd | Password file. For more information, see Chapter 3. |
periodic/ | Directory that contains configuration files for theperiodic utility, which runscron jobs on a regular basis. |
ppp/ | Contains configuration files for Point-To-Point Tunneling Protocol(PPTP). Mac OS X Server only. |
printcap | Printer configuration file for lpd. CUPSautomatically generates this file. For more information, seecupsd(8). |
profile | Global profile for the Bourne-again shell. |
protocols | Network protocol database. |
racoon/ | Directory that contains configuration files forraccoon, the IKE key management daemon. |
rc | Startup script for multiuser mode. |
rc.boot | Startup script for single-user mode. |
rc.cleanup | Cleanup script invoked by /etc/rc. |
rc.common | Common settings for startup scripts. |
rc.netboot | Startup script for booting from the network using NetBoot. |
resolv.conf | DNS resolver configuration. |
resolver/ | Contains files used to resolve hostnames. |
rmtab | Remote NFS mount table. |
rpc | RPC number-to-name mappings. Mac OS X 10.1 and earlier consulted thisfile only in single-user mode, but Mac OS X 10.2 (Jaguar) uses thisfile at other times. For more information, see Chapter 3. |
rtadvd.conf | Configuration file for the router advertisement daemon. For moredetails, see rtadvd(8). |
servermgrd/ | Configuration files for the Server Manager daemon. Mac OS X Serveronly. |
services | Internet service name database. Mac OS X 10.1 and earlier consultedthis file only in single-user mode, but Mac OS X 10.2 (Jaguar) usesthis file at other times. For more information, see Chapter 3. |
shells | List of shells. |
slpsa.conf | Configuration file for the service locator daemon(slpd). |
smb.conf | Samba configuration file. |
smb.conf.template | Template configuration file for Samba. |
squirrelmail/ | Configuration files for SquirrelMail, a web-based email client. Seehttp://www.squirrelmail.org. MacOS X Server only. |
ssh_config | Global configuration file for OpenSSH client programs. |
ssh_host_dsa_key | Private DSA host key for OpenSSH. This file, and the otherssh_host_* files, are created the first time youstart Remote Login in the Sharing System Preferences. |
ssh_host_dsa_key.pub | Public DSA host key for OpenSSH. |
ssh_host_key | Private host key for OpenSSH when using SSH 1 compatibility. |
ssh_host_key.pub | Public host key for OpenSSH when using SSH 1 compatibility. |
ssh_host_rsa_key | Private RSA host key for OpenSSH. |
ssh_host_rsa_key.pub | Public RSA host key for OpenSSH. |
sshd_config | Configuration file for the OpenSSH sshd daemon. |
sudoers | Configuration file for the sudo command. Makesure you use the visudo command only to editthis file. |
syslog.conf | syslogd configuration file. |
ttys | Terminal initialization file. |
ttys.installer | Description not available at time of writing; see errata page athttp://www.oreilly.com/catalog/mosxgeeks. |
watchdog.conf | Configuration file for Mac OS X Server's watchdogservice. Watchdog restarts certain daemons if they die (similar toSystem V inittab). |
webperfcache | File that contains configuration files for Mac OS XServer's webperfcache service,which sits between port 80 and your web server and caches staticpages. |
weekly | Weekly cron job (seecrontab). This is a symlink to/etc/periodic/weekly/500.weekly. |
xinetd.conf | Configuration file for xinetd, the extendedInternet superserver daemon. |
xinetd.d/ | File that contains service-specific configuration files forxinetd. |
xtab | Description not available at time of writing; see errata page athttp://www.oreilly.com/catalog/mosxgeeks. |
A.1.2. The /System/Library Directory
Table A-3 lists the directories storedunder the /System/Library directory. You shouldnot modify the contents of these directories or add new files tothem. Instead, use their counterparts in the/Library folder. For example, to install a newfont, drag it into /Library/Fonts, not/System/Library/Fonts.
Table A-3. The /System/Library directory
File or directory | Description |
|---|---|
Axis/ | Contains support files for Apache Axis. Mac OS X Server only. |
Assistants/ | Contains support files for the setup assistant. Mac OS X Server only. |
Caches/ | Contains caches used by various parts of the operating system. |
CFMSupport/ | Holds shared libraries used by Carbon applications. |
Classic/ | Description not available at time of writing; see errata page athttp://www.oreilly.com/catalog/mosxgeeks. |
ColorPickers/ | Includes localized resources for Mac OS X color pickers. |
Colors/ | Lists the names and values of colors used in the color picker control. |
ColorSync/ | Contains ColorSync profiles. |
Components/ | Contains application building blocks (components), such asAppleScript and color pickers. Components are not applicationsthemselves and are generally shared between applications. |
CoreServices/ | Contains system applications, such asSystemStarter, BootX, theFinder, and the login window. |
Displays/ | Contains ColorSync information for external monitors. |
DTDs/ | Contains document type definitions for XML documents used by thesystem, such as property lists. |
Extensions/ | Holds Darwin kernel extensions. |
Extensions.kextcache | Contains information about extensions in the cache; a compressed XMLdocument. |
Extensions.mkext | Contains the kernel extension cache. It is created at boot by/etc/rc. |
Filesystems/ | Contains drivers and utilities for various filesystems (MS-DOS,AppleShare, UFS, etc.). |
Find/ | Includes support files for Sherlock's contentindexing. |
Fonts/ | Contains core Mac OS X fonts. |
Frameworks/ | Holds a collection of reusable application frameworks, includingshared libraries, headers, and documentation. |
Image Capture/ | Contains device support files for the Image Capture application. |
Java/ | Contains Java class and jarfiles. |
Keyboard Layouts/ | Contains bundles that support internationalized keyboard layouts. |
Keyboards/ | Contains keyboard mappings. |
Keychains/ | Contains system-wide keychain files.(~/Library/Keychains contains per-userkeychains.) |
LoginPlugins/ | Contains helper applications that are launched as you log in. |
Modem Scripts/ | Contains modem configuration scripts. |
MonitorPanels/ | Includes panels used by System Preferences Displays. |
OpenSSL/ | Holds OpenSSL configuration and support files. |
Perl/ | Holds Perl Libraries. |
PHP/ | Contains PHP Libraries. |
PreferencePanes/ | Contains all the preference panes for the Preferences application. |
Printers/ | Contains printer support files. |
PrivateFrameworks/ | Holds private frameworks meant to support Mac OS X. These frameworksare not meant for programmers' use. |
QuickTime/ | Holds QuickTime support files. |
QuickTimeJava/ | Includes support files for the QuickTime/Java bridge. |
Rulebooks/ | Contains information used for text handling, such as word-breakingrules for hyphenation. |
Screen Savers/ | Contains screensavers that you can select from System Preferences Screen Saver. |
ScriptingAdditions/ | Includes AppleScript plug-ins and libraries. |
Server Settings/ | Contains plug-ins for the Server Settings utility. Mac OS X Serveronly. |
ServerSetup/ | Contains support files used when setting the initial serverconfiguration. Mac OS X Server only. |
Services/ | Contains services that are made available through the Services menu. |
Sounds/ | Contains sounds that are available in System Preferences Sound. |
Speech/ | Includes speech recognition and generation support files. |
StartupItems/ | Contains startup scripts as described in Chapter 2. |
SystemConfiguration/ | Contains plug-ins used to monitor various system activities (forApple use only). |
SystemResources/ | Contains precompiled header lists for the C compiler (see Section 5.1.1). |
Tcl/ | Holds Tcl libraries. |
TextEncodings/ | Contains localized text encodings. |
User Template/ | Lists localized skeleton files for user directories. See Section 3.8.3. |
A.1.3. The /Library Directory
Table A-4 lists the contents of the/Library directory. This directory containscounterparts to many directories found in/System/Library. You can use the/Library counterparts for system-widecustomization. If you find a directory of the same name in your homeLibrary directory(~/Library), you can use that for user-levelcustomization. For example, you can install fonts for one particularuser by moving them into~/username/Library/Fonts.
Table A-4. The /Library directory
File or directory | Description |
|---|---|
Application Support/ | Contains support files for locally installed applications. |
Audio/ | Contains audio plug-ins and sounds. |
Authenticators/ | Contains authentication code for locally installed applications. |
Caches/ | Contains cached data used by various parts of the operating system. |
CFMSupport/ | Holds shared libraries used by Carbon applications. |
ColorSync/ | Contains user-installed ColorSync profiles and scripts. |
Desktop Pictures/ | Contains desktop pictures used by System Preferences Desktop. |
Documentation/ | Provides documentation for locally installed applications. |
FTPServer/ | Contains configuration files and the root folderof anonymous FTP server. Mac OS X Server only. |
Filesystems/ | Contains authentication support for the Apple Share network client. |
Fonts/ | Contains locally installed fonts. |
Image Capture/ | Contains locally installed scripts and plug-ins for the Image Captureapplication. |
Internet Plug-Ins/ | Contains locally installed browser plug-ins. |
Java/ | Contains locally installed Java classes (you can drop jar files into/Library/Java/Extensions), as well as a suitabledirectory to use as your $JAVA_HOME(/Library/Java/Home). |
Keyboard Layouts/ | Contains keyboard mappings. |
Logs/ | Holds logs for services such as Apple File Services, the CrashReporter, and the Directory Service. |
Macintosh Manager/ | Contains support files for the Macintosh Manager application (Mac OSX Server only). |
Modem Scripts/ | Holds support files for various modem types. |
Perl/ | Lists locally installed Perl modules (MakeMaker'sINSTALLSITELIB). |
PreferencePanes/ | Contains system preference panes for locally installed utilities suchas TinkerTool. |
Preferences/ | Lists global preferences. |
Printers/ | Lists printer drivers and utilities. |
QuickTime/ | Contains locally installed QuickTime components. |
QuickTimeStreaming/ | Contains the QuickTime Streaming Server (Mac OS X Server only). |
Receipts/ | Leaves a receipt in the form of a .pkg directoryafter you install an application with the Mac OS X installer. The.pkg directory contains a bill of materials file(.bom), which you can read with thelsbom command. |
Screen Savers/ | Lists locally installed screensavers. |
Scripts/ | Contains a variety of AppleScripts installed with Mac OS X. |
StartupItems/ | Lists locally installed startup items. See Section 2.2. |
Tomcat/ | Holds the Apache Tomcat Java Servlet and JSP server (Mac OS X Serveronly). |
User Pictures/ | Contains user pictures that are used in the login panel. |
WebServer/ | Contains the Apache CGI and document rootdirectories. |
A.1.4. The /var Directory
The /var directory contains transient andvolatile files, such as PID files (which tell you the process ID of acurrently running daemon), log files, and many others. Table A-5lists the contents of the /var directory.
Table A-5. The /var directory
File or directory | Description |
|---|---|
at/ | Contains information about jobs scheduled with theat command. |
backups/ | Contains backups of the NetInfo database. |
cron/ | Contains user crontab files. |
db/ | Includes a grab bag of configuration and data files, including thelocate database, the NetInfo database, andnetwork interface information. |
empty/ | Description not available at time of writing; see errata page athttp://www.oreilly.com/catalog/mosxgeeks. |
log/ | Contains a variety of log files, includingsyslog, mail, and web server logs. |
mail/ | Contains inboxes for local users' email. |
msgs/ | Holds system-wide messages that were delivered using msgs-s. |
named/ | Includes various files used for local DNS services. |
netboot/ | Contains various files used for NetBoot. |
root/ | Serves as the root user's homedirectory. |
run/ | Holds PID files for running processes. Also contains working filesused by programs such as sudo. |
rwho/ | Contains information used by the rwho command. |
servermgrd/ | Contains runtime files used by the Server Manager daemon. Mac OS XServer only. |
spool/ | Serves as a spool directory for mail, printer queues, and otherqueued resources. |
tmp/ | Serves as a temporary file directory. |
vm/ | Contains your swap files. |
yp/ | Contains files used by NIS. |
A.1.5. The /dev Directory
The /dev directory containsfiles that represent devices attached to the system, includingphysical devices, such as serial ports, and pseudodevices, such as arandom number generator. TableA-6 lists the contents of the /dev directory.
Table A-6. The /dev directory
File or directory | Description |
|---|---|
bpf[0-3] | Berkeley Packet Filter devices. See bpf(4). |
console | The system console. This is owned by whoever is currently logged in.If you write to it, the output will end up in/var/tmp/console.log, which you can view withthe Console application(/Applications/Utilities). |
cu.modem | Modem device for compatibility with the Unix cu(call up) utility. |
disk[0-n] | Disk. |
disk[0-n]s[0-n] | Disk partition. For example, /dev/disk0s1 is thefirst partition of /dev/disk0. |
fd/ | Devices that correspond to file descriptors. See thefd manpage for more details. |
klog | Device used by syslogd to read kernel messages. |
kmem | Image of kernel memory. |
mem | Image of the system memory. |
null | Bit bucket. You can redirect anything here, and it will disappear. |
ptyp[0-f] | Master ends of the first sixteen pseudo-ttys. |
pty[q-w][0-f] | Master ends of the remaining pseudo-ttys. |
random | Source of pseudorandom data. See random(4). |
rdisk[0-n] | Raw disk device. |
rdisk[0-n]s[0-n] | Raw disk partition. |
stderr | Symbolic link to /dev/fd/2. |
stdin | Symbolic link to /dev/fd/0. |
stdout | Symbolic link to /dev/fd/1. |
tty | Standard output stream of the current Terminal or remote login. |
tty.modem | Modem device. |
ttyp[0-f] | Slave ends of the first sixteen pseudo-ttys. |
tty[q-w][0-f] | Slave ends of the remaining pseudo-ttys. |
urandom | Source of pseudorandom data, not guaranteed to be strong. Seerandom(4). |
vn[0-3] | Pseudo disk devices. |
zero | Infinite supply of null characters. Often used withdd to create a file made up of nullcharacters. |
| IV. Appendixes | B. Command-Line Tools: The Missing Manpages |
Copyright © 2003 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.
